JWT signing algorithms overview
Explore JSON Web Token (JWT) signing algorithms, covering two of the most popular asymmetric encryption approaches: RSA and EC. Learn about the pros and cons of each algorithm and how Logto uses them to secure your JWT tokens.
What is a JWT?
JSON Web Token (JWT) is a compact, URL-safe way to represent claims securely. The structure includes a header, payload, and signature.
Nowadays, JWTs have been widely adopted and play a crucial role in OAuth 2.0 and OIDC. But how does an authorization server verify and trust a JWT sent from a client? How is the token issued and signed by the issuer? In this blog post, we'll talk about asymmetric encryption and delve into the pros and cons of different signing algorithms that Logto uses in its JWT tokens.
JWT structure
Logto signs all JWT tokens, including both ID tokens and access tokens. A signed JWT is also known as a JWS (JSON Web Signature). A signed JWT structure consists of three parts: the header, payload, and signature, separated by dots (.).
JOSE (JSON Object Signing and Encryption) header
The header typically consists of the following parts:
- typ: The type of the token, which is JWT.
- alg: The signing algorithm being used, such as RS256 or ES384.
- kid: A hint indicating which key was used to secure the JWT.
Payload
The payload contains the claims, which are statements about an entity (typically, the user) and additional data. For example an ID token might contain the following claims:
Signature
The signature is used to verify that the sender of the JWT is not an imposter and that the message has not been tampered with. When using a signed JWT, you must verify the token signature to ensure the token's integrity. Check this guide on how to validate JWT tokens to protect your API.
What is asymmetric encryption?
Asymmetric encryption, also known as public-key cryptography, a foundational concept in computer security and cryptography, involves the use of a unique pair of related keys: a public key and a private key.
Definitions of public and private keys
- Public key: The public key, as the name suggests, is designed for open sharing. In the context of JWT and similar systems, the public key is used for signature verification, not encryption. When data is signed with the private key and the recipient possesses the corresponding public key, they can validate that the data was indeed signed by the private key holder and has not been tampered with during transmission.
- Private key: In contrast, the private key is a closely guarded secret that should only be known to its rightful owner. In the context of JWT, the private key is used to create digital signatures that can be verified by anyone with access to the corresponding public key.
This unique arrangement of keys, forms the basis of secure data transmission and user authentication mechanisms in the digital world. Check this blog post for more details.
Popular JWT signing key algorithms: RSA vs EC
The RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adelman) and EC (Elliptic Curve) algorithms are the two most commonly used “mathematical functions” in asymmetric encryption.
As developers, we are often presented with a choice between these algorithms when dealing with an auth framework and its JWTs. But which one would be your choice? Let’s delve into the pros and cons of each.
RSA signing algorithm (E.g. RSASHA256)
- Pros:
- Widespread support: RSA is widely supported across various platforms and libraries, ensuring compatibility in a wide range of environments.
- Long track record: RSA has a long history of reliable security, and its algorithms are well-understood by the cryptographic community.
- Cons:
- Key sizes: RSA keys are longer to achieve the same level of security as EC, resulting in larger token sizes and increased computational overhead.
- Performance: RSA operations tend to be slower than EC, which can be a drawback in high-traffic applications.
EC signing algorithm (E.g. ECDSASHA384)
- Pros:
- Efficiency: EC boasts superior performance compared to RSA, making it ideal for applications with resource constraints or high traffic loads.
- Compact key sizes: EC keys are way shorter than their RSA counterparts while offering equivalent security levels. This leads to reduced storage and network requirements and accelerated cryptographic operations.
- Security: EC is highly regarded for its robust security, fortified by the intricate mathematics behind elliptic curves, rendering it resilient against brute-force attacks.
- Cons:
- Limited support: Some older systems and libraries may lack comprehensive EC support, potentially causing compatibility issues. E.g. Cloudflare Zero Trust does not support EC signed tokens.
- Complexity: Implementing EC can be more intricate due to the mathematical intricacies involved.
Logto's choice of JWT signing algorithms
Logto has always been committed to the highest standards of security and flexibility and tends to use the most modern and performant solutions at its core. EC offers a winning combination of robust security and computational efficiency, making it an ideal fit for modern authentication and authorization needs. Therefore, EC has been our default signing key algorithm since the early stage of our product.
However, we've also acknowledged that the EC-signed tokens are not compatible with some third-party systems and frameworks, especially the legacy ones. Hence, we have also introduced a feature to change your JWT signing key algorithm by rotating your private keys.
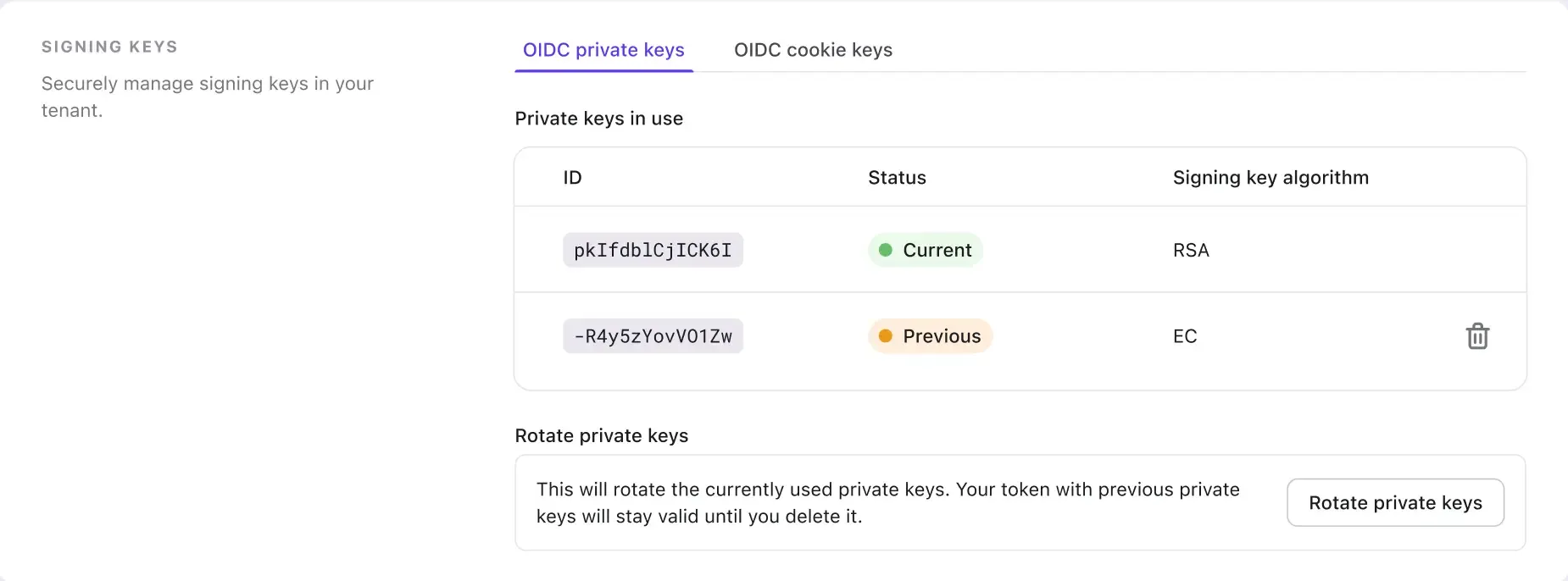
So if you are facing the problem of not being able to connect to a third-party platform due to the unsupported JWT signing algorithm, now it's time to rotate and select the RSA algorithm for your new private key.
This feature also helps mitigate the risks associated with long-term key exposure or compromise. Regularly rotating private keys should be a fundamental practice in any organization's security strategy and is highly recommended by Logto.
Recap: The commonly used JWT signing algorithms: RSA and EC
Signing JWT tokens ensures the integrity and authenticity of the data being transmitted. The choice of signing algorithm can have a significant impact on the security, performance, and compatibility of your application.
Both RSA and EC algorithms are essential and popular algorithms in cryptography. Understanding the pros and cons and the mathematical principles behind these algorithms helps make better decisions for your application to work with an authentication and authorization framework.
Logto will continue to explore and offer you a more secure and robust user experience.